In the food and beverage industry, membrane filtration is a commonly used process to increase the value of various plant-based and dairy products and facilitate the reuse of water. Many products are produced through the process of membrane filtration, including whey protein concentrate and yogurts. It’s also used to concentrate plant-based proteins and extract water from fruit and milk products for reuse.
There are several types of materials that are used depending on the membrane filtration method. Here we’ll review these materials and their role in the membrane filtration process.
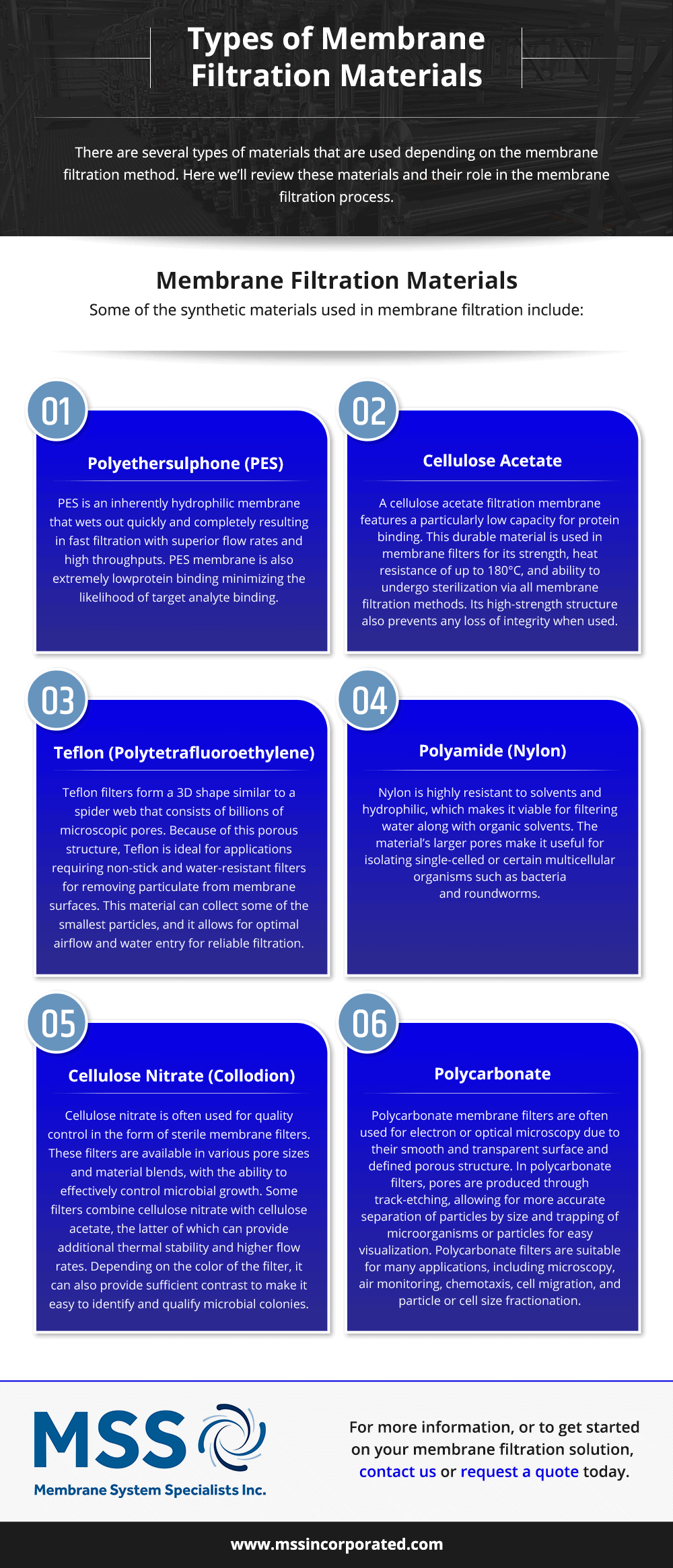
Membrane Filtration Materials
Some of the synthetic materials used in membrane filtration include:
Polyethersulphone (PES)
PES is an inherently hydrophilic membrane that wets out quickly and completely resulting in fast filtration with superior flow rates and high throughputs. PES membrane is also extremely low protein binding minimizing the likelihood of target analyte binding.
Cellulose Acetate
A cellulose acetate filtration membrane features a particularly low capacity for protein binding. This durable material is used in membrane filters for its strength, heat resistance of up to 180°C, and ability to undergo sterilization via all membrane filtration methods. Its high-strength structure also prevents any loss of integrity when used.
Teflon (Polytetrafluoroethylene)
Teflon filters form a 3D shape similar to a spider web that consists of billions of microscopic pores. Because of this porous structure, Teflon is ideal for applications requiring non-stick and water-resistant filters for removing particulate from membrane surfaces. This material can collect some of the smallest particles, and it allows for optimal airflow and water entry for reliable filtration.
Polyamide (Nylon)
Nylon is highly resistant to solvents and hydrophilic, which makes it viable for filtering water along with organic solvents. The material’s larger pores make it useful for isolating single-celled or certain multicellular organisms such as bacteria and roundworms.
Cellulose Nitrate (Collodion)
Cellulose nitrate is often used for quality control in the form of sterile membrane filters. These filters are available in various pore sizes and material blends, with the ability to effectively control microbial growth. Some filters combine cellulose nitrate with cellulose acetate, the latter of which can provide additional thermal stability and higher flow rates. Depending on the color of the filter, it can also provide sufficient contrast to make it easy to identify and qualify microbial colonies.
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate membrane filters are often used for electron or optical microscopy due to their smooth and transparent surface and defined porous structure. In polycarbonate filters, pores are produced through track-etching, allowing for more accurate separation of particles by size and trapping of microorganisms or particles for easy visualization. Polycarbonate filters are suitable for many applications, including microscopy, air monitoring, chemotaxis, cell migration, and particle or cell size fractionation.
Partner with Membrane System Specialists, Inc.
Membrane System Specialists, Inc. provides membrane filtration systems and materials to meet your fluid separation needs while complying with strict sanitation standards. Our membrane filtration systems are capable of removing particles from less than 0.001 microns up to 10 microns. We construct our equipment using durable materials that are easy to clean and require minimal maintenance.
At Membrane Specialists, Inc., we cover every step of the design process to develop the ideal final product based on your specific requirements. We also provide installation, training, commissioning, and support to ensure you get the most from your equipment.
For more information, or to get started on your membrane filtration solution, contact us or request a quote today.


Comments are closed